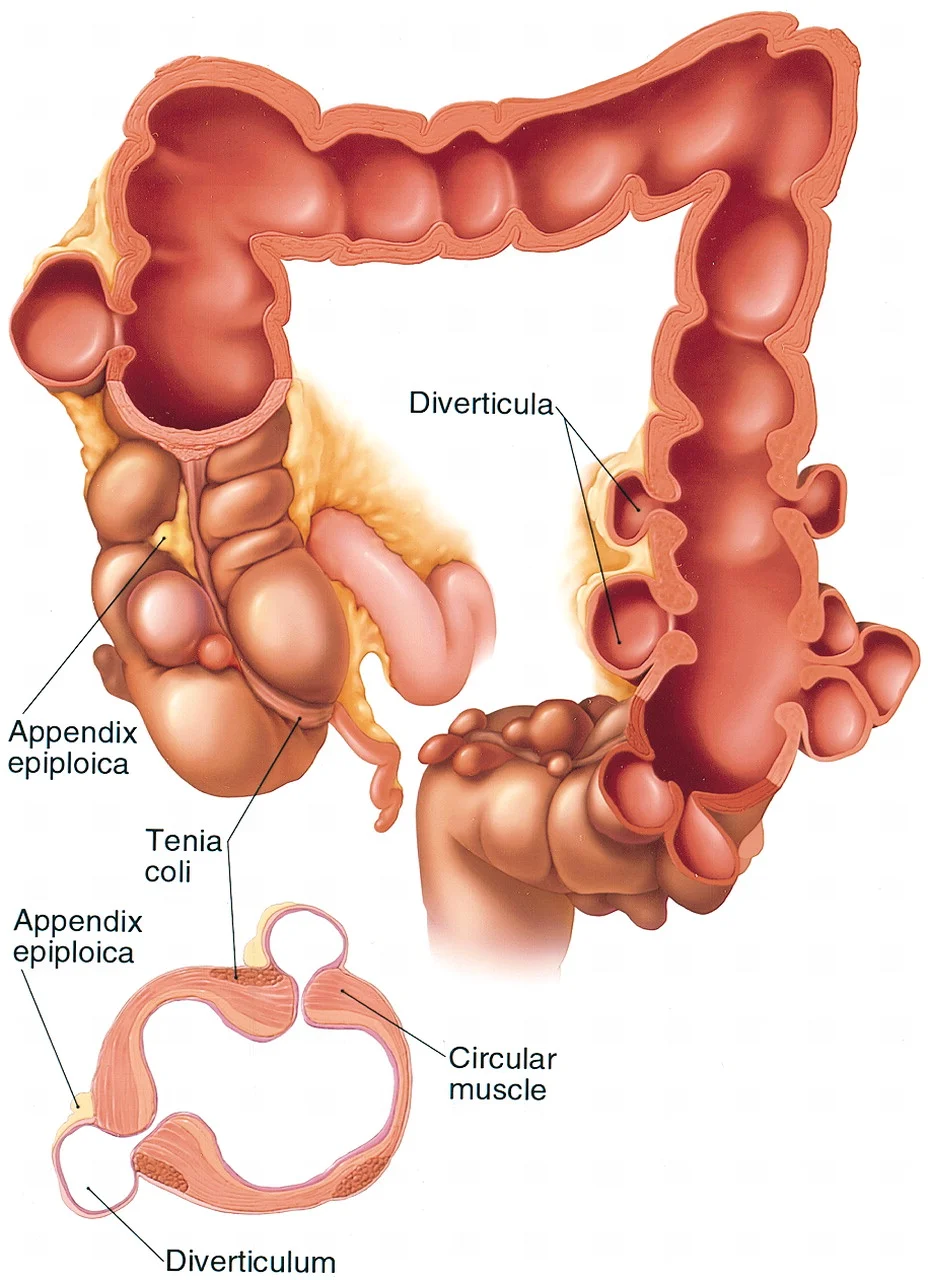
Without adequate fiber and water intake, a patient’s stool can become hard and more difficult to move through the colon. As the muscles work harder, the extra pressure exerted on the colon wall, causes the colon wall to bulge out and form pouches. These pouches are called diverticula. Usually these pouches remain asymptomatic, but they can result in occasional cramping, bloating, constipation, diarrhea and rectal bleeding.
Diverticulosis can usually be treated with a high-fiber, well-hydrated diet
If the diverticula become infected or inflamed, they can swell and possibly rupture. This condition is called diverticulitis. Patients usually have pain, fever, chills, cramping, bloating, constipation or diarrhea. In mild cases, patients can be treated as outpatients with oral antibiotics, bowel rest and dietary changes. However if the condition is serious, patients may need to be admitted for intravenous antibiotics. Sometimes, when the colon ruptures patients may develop an abscess which may need to be drained to remove the pus. In patients who have had a perforation or in patients who have two or more attacks, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected area of the colon. Left sided symptoms are the most common, but diverticulitis can occur in any part of the colon.
treatment options
To treat recurrent or complicated diverticulitis, surgical removal of the affected portion of the colon is necessary. After the affected portion of the colon is removed, the colon is reconnected and normal bowel function is restored. Read some patient testimonials here.
surgery prep
Prior to surgery, we will check if the rest of your colon is healthy or if it has any other issues that should be addressed. Patients are scheduled for colonoscopies prior to any colon surgery which can usually be scheduled the day before your surgery. Learn more here.
surgical techniques
At the Colorectal Clinic of Tampa Bay, we are trained in the most advanced techniques to perform all colon surgeries using minimally invasive techniques. This means less pain and decreased hospital stays.